Nothing is as obvious as the fact that humanity is made up of diverse entities. Even among those who identify as a group with shared value systems and beliefs, we are all different albeit with some measure of similarities. Over time, psychologists and social scientists who have concerned themselves with studying and understanding human behaviors and personality have categorized people under what they regard as the four basic personality types: You are either majorly phlegmatic, sanguine, melancholic, or choleric in nature. Apart from the four temperament theory, there is also what’s known as the Big Five personality traits and the 16 MBTI personality types.
As its name suggests, the former advocates that there are five broad dimensions to personality traits: extraversion, agreeableness, openness, conscientiousness, and neuroticism. Like the four temperament theory and the Big Five personality traits, Myers-Briggs Type Indicator (MBTI) seeks to explain how people are different and why they like what they like. While the propounders of these psychological trait theories have different postulations, they are inherently saying the same thing: that people are different and that understanding these differences is of far-reaching benefits to an individual and the society at large.
The Origin of Myers-Briggs Type Indicator (MBTI) and What Its 16 Personality Types Entail
The MBTI builds upon the psychological types highlighted by C. G. Jung, the Swiss psychiatrist that created analytical psychology. Jung was also a psychoanalyst and one of the things he is still remembered for is his book titled Psychological Types. Originally published in German in 1921, the books hypothesized that there are four major functions of consciousness: Sensation, Intuition, Thinking, and Feeling. According to him, the first two are the perceiving/non-rational functions of consciousness while the last two are the judging/rational functions. The psychoanalyst went further to postulate that the four functions of consciousness are influenced by two major attitude types: extraversion and introversion.
Now, the original versions of the MBTI as created by Katharine Cook Briggs and her daughter, Isabel Briggs Myers, were derived from what Jung stipulated in his book. Katharine who had been studying personality realized that Jung’s four functions of consciousness were similar to the four temperaments she had proposed: Social, Executive, Spontaneous, and Thoughtful. With that, Katharine and her daughter went about studying Jung’s works. First, they identified the basic personality preferences (what people like) of each of the four functions of consciousness that Jung posited. Thereafter, they put forward 16 unique personality types derived from interactions among the preferences.
A Breakdown of The 16 MBTI Personality Types
In a nutshell, your personality type simply means what you prefer and really like. It is believed that an understanding of one’s personality is tantamount to an awareness of how different you are from people around you, how you behave, your perspective of the world around you, and whatnot. In essence, it can help you have a better relationship with people and improve your productivity, sense of worth, and quality of life as a person. The following are the 16 MBTI personality types.
The MBTI Extraversion Personality Types
There are a total of eight extroverted personality types and each of them is unique but with some similar attributes. The defining feature of people that belongs to the MBTI extraversion personality types is that they derive energy from involving themselves in activities and being around people. They normally have many friends and are often described as “outgoing”.
1. ESTP (Extraversion, Sensing, Thinking, and Perception)
People under this personality type are generally outgoing and action-oriented. They are open to change and tolerant as much as they are spontaneous and would rather solve problems by taking immediate action instead of trying to understand the problem first. They’d rather do something and learn how it shouldn’t be done than spend time learning how it should be properly done.
2. ESFP (Extraversion, Sensing, Feeling, and Perception)
While they are free-sprits, adventurous, and enjoy the notion of being independent, ESFPs really like people and dislikes being alone or working alone. People with this personality type are accepting, friendly, and readily willing to adapt to new environments. They are exuberant lovers of people and are more likely to describe a new way of life they encounter as intriguing rather than shocking.
3. ENFP (Extraversion, Intuition, Feeling, and Perception)
Almost always enthusiastic, ENFPs are confident people, yet they seek affirmation from people around them. People who fall under this category are quite imaginative; they see opportunities wherever they find themselves and are very supportive friends and relatives. They are good at making improvisations just as it is easy for them to understand complex situations.
4. ENTP (Extraversion, Intuition, Thinking, and Perception)
To sustain the interest of ENTPs, one has to constantly throw new challenging problems at them. They are easily bored by routine but are strategic thinkers and often come up with stimulating and ingenious ideas. People grouped here are generally creative and bold; they wouldn’t be held back from expressing what they feel or think and are always regarded as productive in any group they find themselves in.
5. ESTJ (Extraversion, Sensing, Thinking, and Judgment)
People of this personality type are known to be straightforward and practical. They seem to be naturally realistic with their aspirations and wouldn’t compromise on standards they consider to be ideal. ESTJs are committed to being what they expect from people. Although they are accomodating and friendly, they wouldn’t tolerate anyone they deem as dishonest, disrespectful, and uncooperative.
6. ESFJ (Extraversion, Sensing, Feeling, and Judgment)
Sympathetic and kind, ESFJs are also known for being conscientious and collaborative individuals. They dislike being in an acrimonious environment and seem to be always committed to having the people around them on good terms with each other. People that belong to this personality type are loyal friends; they can go out of their way to assist people and make them feel comfortable. It is also important for them to be recognized and appreciated for who they are.
7. ENFJ (Extraversion, Intuition, Feeling, and Judgment)
A rare personality, especially among men, ENFJ are warmhearted, loyal, and empathetic like the ESFJs. It is hard for them to give up on people and are always committed to the advancement of any group they belong to. They are good leaders, sociable, and praising them can make them much more helpful to their environment just as criticisms stir them to do more to gain positive recognition.
8. ENTJ (Extraversion, Intuition, Thinking, and Judgment)
A common attribute found in people of this personality type is the willingness to assume leadership positions. They are strong-willed with the ability to make quick and effective decisions. Also assertive with their ideas, ENTJs are open and honest. They are also known to be skilled in finding solutions to problems, thanks to their unrelenting quest for knowledge.
The MBTI Introversion Personality Types
The Introversion personality types are also eight in number. Each of them is unique with peculiar defining attributes. Yet, individuals categorized here are known to prefer doing things alone and majorly derive their energy internally. They majorly live in their heads and are often described as “reserved”.
9. INTP (Introversion, Intuition, Thinking, and Perception)
INTPs are people of logical minds; they need to find an analytical and insightful way of interpreting things around them. They are often described as abstract and theoretical entities who are attracted to thoughts and suppositions. Even though they can adapt to changing circumstances and are flexible, these individuals are not excited about having social interactions.
10. INFP (Introversion, Intuition, Feeling, and Perception)
INFP is also a rare personality trait among people who are generally introverted, prospecting, and intuitive. INFPs are curious individuals who are idealistic in nature as much as they are eager to understand people around them and help them actualize their goals. People with this personality are true to their values, open to changes, and very cooperative; unless it has become a threat to their ideals and value systems.
11. ISFP (Introversion, Sensing, Feeling, and Perception)
Individuals grouped under this MBTI personality type are private but affable, good-natured, and sensitive. ISFPs wouldn’t force their opinions on people as much as they would do anything within their ability to evade conflicts. They are committed to the present and like to be in control of their space and time. People that belong to this group are not quick decision-makers as they like considering all the options available.
12. ISTP (Introversion, Sensing, Thinking, and Perception)
Also private individuals, ISTPs are analysts who are unprejudiced and open-minded. Mostly common among men, they are known to be difficult to manipulate and straightforward. ISTPs are thorough in making decisions and are interested in knowing the cause of a problem as much as they are eager to find solutions. People that belong to this MBTI personality type can be individualistic to a fault.
13. INTJ (Introversion, Intuition, Thinking, and Judgment)
INTJs have traits that are conflicting and confusing for people to understand but intrinsically, they are known to be strong-willed and focused on pursuing their dreams and attaining their goals. People grouped here are individualistic as much as they are difficult to convince. Although they are curious and open to new ideas, INJTs are always rational in their actions, introverted, but with a very complex mind. They are difficult to fool.
14. INFJ (Introversion, Intuition, Feeling, Judgment)
This MBTI personality type revolves around people who are decisive and organized in pursuing their aspirations. They are loyal to their values, conscientious, and independent. Nonetheless, they seek to build meaningful relationships and are indeed all out to make meaning out of everything. INFJs are very thoughtful about life, the essence of actions, reactions, and events.
15. ISFJ (Introversion, Sensing, Feeling, and Judgment)
The people grouped here are introverted, friendly, and quiet but very observant. ISFJs are considerate in their dealings, committed to their endeavors, and always strive to get things right. It is difficult for them to not consider people’s feelings while making decisions. Because of this, they are known as “The Protectors” among the other MBTI personality types. They are also responsible individuals who desire a peaceful and orderly atmosphere at all times.
16. ISTJ (Introversion, Sensing, Thinking, and Judgment)
Privacy is of huge importance to ISTJs and they go about their day-to-day activities with great care and attention to detail. People that are grouped here are often described as serious and focus. They are straightforward, unemotional, and would only engage practical ideas. One of the most dominant personalities, these people are regarded as logisticians due to their unrelenting drive to be logical and dedicated to a course while upholding their integrity.
MBTI Compatibility: What Personality Type Don’t Like Each Other?
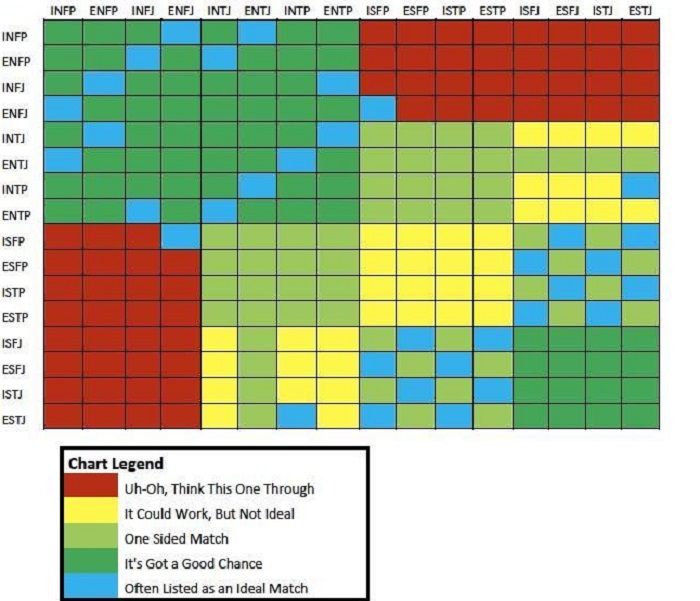
In accordance with the attributes of the 16 MBTI personality types discussed above, people have found the categorization useful in determining their ideal partners at work, romantic partners, and what have you. The relationships between each of the types are unique and many are cordial and easy-going as much as some seem to be naturally bound for disaster.
The table below captures all the MBTI personality types that are not compatible.
| INFP – ISFP | ENFP – ISFP | INFJ – ISFP | ENFJ – ESFP |
| INFP – ESFP | ENFP – ESFP | INFJ – ESFP | ENFJ – ISTP |
| INFP – ISTP | ENSP – ISTP | INFJ – ISTP | ENFJ – ESTP |
| INFP – ESTP | ENFP – ESTP | INFJ – ESTP | ENFJ – ISFJ |
| INFP – ISFJ | ENFP – ISFJ | INFJ – ISFJ | ENFJ – ESFJ |
| INFP – ESFJ | ENFP – ESFJ | INFJ – ESFJ | ENFJ – ISTJ |
| INFP – ISTJ | ENFP – ISTJ | INFJ – ISTJ | ENFJ – ESTJ |
| INFP – ESTJ | ENFP – ESTJ | INFJ – ESTJ |
According to the MBTI postulations, a combination of people of different personality types as shown above is most likely to result in a rocky relationship. However, this does not mean they can’t get along. With a good understanding of each other’s preferences, they can have a good relationship.
What Is The Happiest Personality Type?
Based on the 16 distinctive personalities of the Myers-Briggs Type Indicator, several establishments have conducted surveys that concluded on a general scale that people of extraversion personalities are happier than those of introversion personalities. One of such surveys conducted by Truity Psychometrics found that ESFJs are the most satisfied and happiest at work.
It is believed that the ESFJs and ESFPs are the happiest because they are generally satisfied with their life choices. As detailed above, people of these personalities are free-spirited and collaborative. It is easy for them to get along with people; they enjoy social gatherings and are not critical thinkers. All of these traits facilitate a deep sense of satisfaction within them which in turn, fuels their happy nature.
Which Personality Type Is The Meanest?
For someone to be regarded as mean, s/he must have a vicious or aggressive behavior that most people would consider to be unkind to the people around him/her, spiteful, and unkind. Having that in mind, it wouldn’t be out of place to conclude that anyone with the MBTI personality traits that feature “Feeling” can’t be the meanest of individuals: they are known to regard people’s feelings.
With that, we can eliminate ESFPs, ENFPs, ESFJs, ENFJs, INFPs, ISFPs, INFJs, and ISFJs. Narrowing it down can be tricky as what’s mean can be subjective. Nonetheless, the question was asked on PersonalityCafe and most people voted ESTJs as the meanest MBTI personality type; followed by ENTJs, ESTPs, and then ENTPs. As discussed above, ESTJs are straightforward and realistic individuals; so it’s quite easy to see that they can easily offend people.
INFJ Is The Rarest MBTI Type and ISFJ The Most Common
People get to know which of the 16 personality types they belong to by taking the MBTI assessment. Based on the population of the people who have taken the test thus far, it has been concluded that the INFJ is the rarest personality type. As of 2017, the population of the United States was at 325.1 million. Out of that massive figure, it is said that only 1.5 percent (4,876,500) are INFJs.
Apart from the INFJs, other rare personality types include ENTJ (1.8%), INTJ (2.1%), ENFJ (2.5%), ENTP (3.2%), INTP (3.3%), ESTP (4.3%), INFP (4.4%), and ISTP (5.4%). The most common group are the ISFJs (13.8%) followed by the ESFJ (12%), ISTJ (11.6%), ISFP (8.8%), ESTJ (8.7%), ESFP (8.5%), and ENFP (8.1%).
INFPs Are Mostly Attracted to ENFJs and ENTJs
While they are poised to easily understand and get along with people, INFPs are not very compatible with ESTJs, ISTJs, ESFJs, ISFJs, ESTPs, ISTPs, ESFPs, and ISFPs. Apart from these, they can relate well with people of other MBTI types but are mostly known to be fond of ENFJs and ENTJs. Their connection with people from the latter group has been linked to the confident and resolute character of the ENTJs, augmented by their innate ability to be open and honest.
For the ENFJs, it’s their loyal and empathetic nature that leaves them striving to help people around them. These traits are also the defining attributes of INFPs who are committed to helping people and being loyal to their values. INFPs, ENFJs, and ENTJs are instinctive and it is one of the common grounds upon which they forge a relationship.
Given their attraction to people of intelligent minds and the resolute to lead a meaningful lifestyle, INFPs seek to have a deep-seated connection with their romantic partners. As such, they would hardly involve themselves in casual relationships. It is important for this group of people to feel close to the people they love, to share a serious bond with them, and be a part of their innermost thoughts.
Can You Belong To Two MBTI Types?
When you take the MBTI assessment, you can get results that suggest you belong to two or more MBTI types. But then, one of them has a better description of your person. To find your true MBTI, you can note your result and retake the test. Alternatively, you can study the MBTI types listed in your result. Doing this, you will realize that some of the attributes described aren’t characters you’d associate with yourself. Eliminate the traits that are odd to you and you will narrow down your type.
Each of the 16 types is unique, even though some may seem to be very similar. Studying the traits of the types you have been grouped under would help you understand their dissimilarities. Thereafter, it is only a matter of asking yourself which of the types best describes you. For instance, the traits of INTP and ISTP might seem to be describing the same group of people but there are underlying qualities that set them apart.
Which MBTI Type Is The Saddest?
Just as the 16 types are different, what makes them sad are also different. Among people of extraversion personalities who are said to be generally happier than the introversions, the things that make them unhappy range from inability to meet their loved ones need to failure in connecting with people, sensing disloyalty, the feeling of guilt over people’s sufferings, unaccomplished goals, feeling powerless, uncared for, and neglected.
As culled from the MBTI Manual, a global study showed that the INFPs are the least happy and less satisfied with life. Various platforms have expressed that the INFPs loathe seeing people being mistreated; they believe in fairness and are left depressed and sad when they withness injustice around them. With the negative reports of human rights abuse reported across the globe daily, it is not difficult to see why the INFPs are the saddest.
Which MBTI Type Has The Lowest IQ?
Albeit it has been contended in some quarters that a person’s personality isn’t a factor that determines how intelligent s/he is, people have relentlessly pointed out that intelligent people are most likely to be found in a particular MBTI personality type. While this is still up for debate, it is widely held that INTPs and ENTPs have higher intelligence quotients compared to others.
Some studies have validated this supposition to some extent. One of such examined the relationship between the MBTI personalities and IQ level. It was hypothesized that people who are intuitive and thoughtful would be more intelligent than those who rely on their feelings, and the results were consistent with the hypothesized relationships.
Which MBTI Type Is The Most Evil?
As far as we can tell, any of the 16 MBTI personality types can be evil just as all have good traits. Since there are no wrong personality preferences, being evil is more of what you choose to do rather than who you are. In fact, it has been suggested that people are inherently good.
However, it has been circulated in some quarters that the ENTJ is the evilest MBTI type. The question was posed on Typology Central where most of the votes went to the ENTJs. It is imperative to stress that there has not been any credible validation of this notion. Each of the MBTI personality types has attributes that are positive and destructive if unchecked.

